MariaDB Cluster (Multi-Master) Peformance on ARM
During our last blog post we explored the mariadb on arm cluster performance in master-slave mode. In this blog post, we will explore mariadb on arm cluster performance in multi-master mode. MariaDB Server has an in-built support for Multi-Master setup using galera synchronous replication. Users who can’t afford slave lag continue to opt for multi-master solution that can also help aid write-scalability if load could be distributed (with reduced overlap).
Setup
Let’s first understand setup
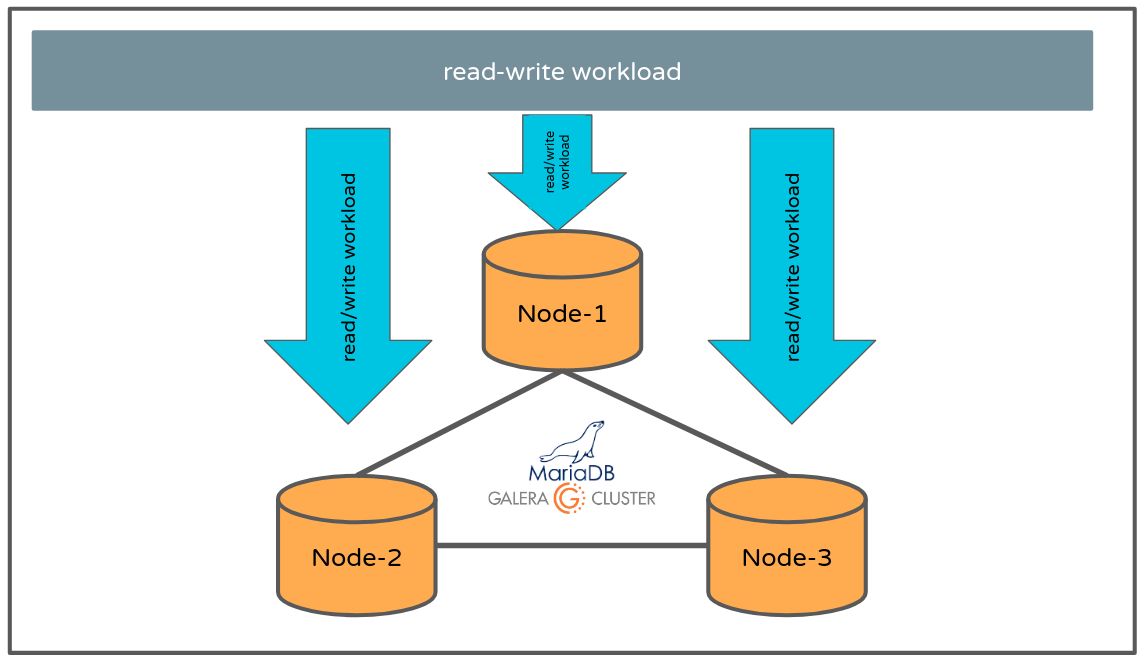
- 3 nodes mariadb multi-master cluster. (node-1/2/3). All nodes are on-par with the same capability.
- We have 3 different setups:
- read-write workload: write-workload on node-1 and read-workload on node-2 and node-3. (most common found setup).
- write-to-one-node: node1 (write-workload), node-2 and node-3 (no explicit workload).
- write-to-all-nodes: node-1, node-2, node-3 (write workload simultaneously active on all nodes with possible conflicts/overlap).
- Server:
- MariaDB-10.6 (10.6.1 (beta)).
- Nodes Compute Configuration (Cost-Performance Model).
- 16 vCPU ARM (Kunpeng 920 2.6 Ghz)
- 10 vCPU x86 (Intel(R) Xeon(R) Gold 6151 CPU @ 3.00GHz)
- Storage/OS:
- NVME SSD with the same IOPS, CentOS-7
- Configuration details: click here [additional command line –skip-log-bin –wsrep-on=1]
- Same repo also has a script that I have used for running the said workload.
- Same repo also has a script that I have used for running the said workload.
Benchmark and Analysis
read-write workload
benchmarking pattern
- write workload is executed on node-1 and read-workload on node-2 and node-3. node-2 and node-3 continue to apply replica-sets from node-1.
- Given synchronous replication, if node-2 or node-3 are unable to keep up with the replicated traffic, a flow-control signal is sent that could momentarily pause node-1 processing of the event. So the experiment also captures the flow-control pause to help re-validate the performance facts.
- Each run is with increasing scalability 1-128 threads. Workload runs for 60 secs followed by 20 seconds of sleep.
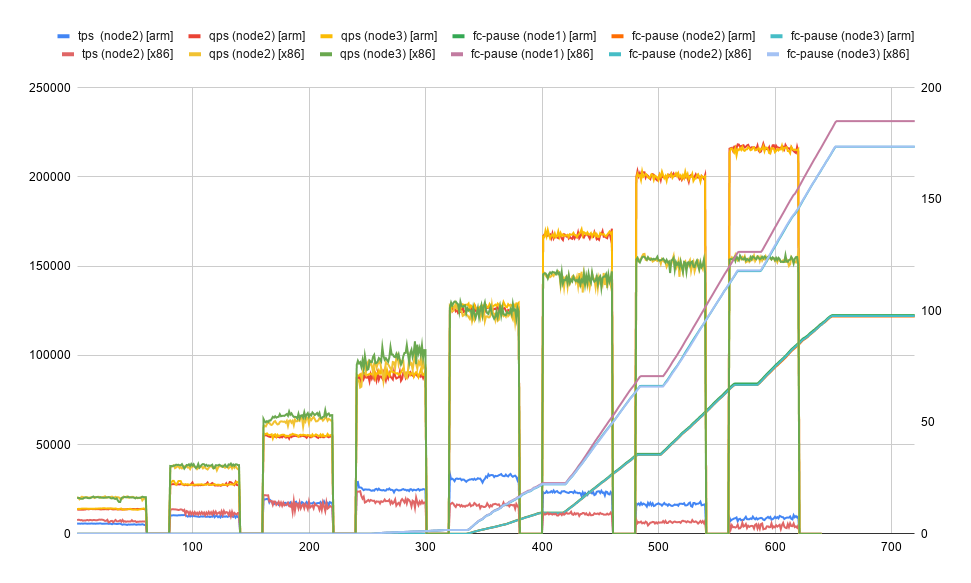 left-y axis tracks qps/tps, right-y axis flow-control-pause (in seconds) and x axis timeline
left-y axis tracks qps/tps, right-y axis flow-control-pause (in seconds) and x axis timeline
observations
- mariadb on arm continues to scale better for both read and write workload.
- improved flow control (in arm case) means read nodes are able to service latest replicated data more quickly.
- take-away: for the same cost better performance and importantly more up-to-date data for read-nodes.
write-to-one-node
benchmarking pattern
- Simplest scenario where-in write is done to only one node and it is internally replicated to the other nodes. Since other nodes don’t have read-traffic they are just left to apply the said replicated workload. Ideally, given all nodes are on-par and replicated nodes are applying the processed replica-sets, there should be negligible flow control pause originating from replica-nodes.
- Each run is with increasing scalability 1-128 threads. Workload runs for 60 secs followed by 20 seconds of sleep.
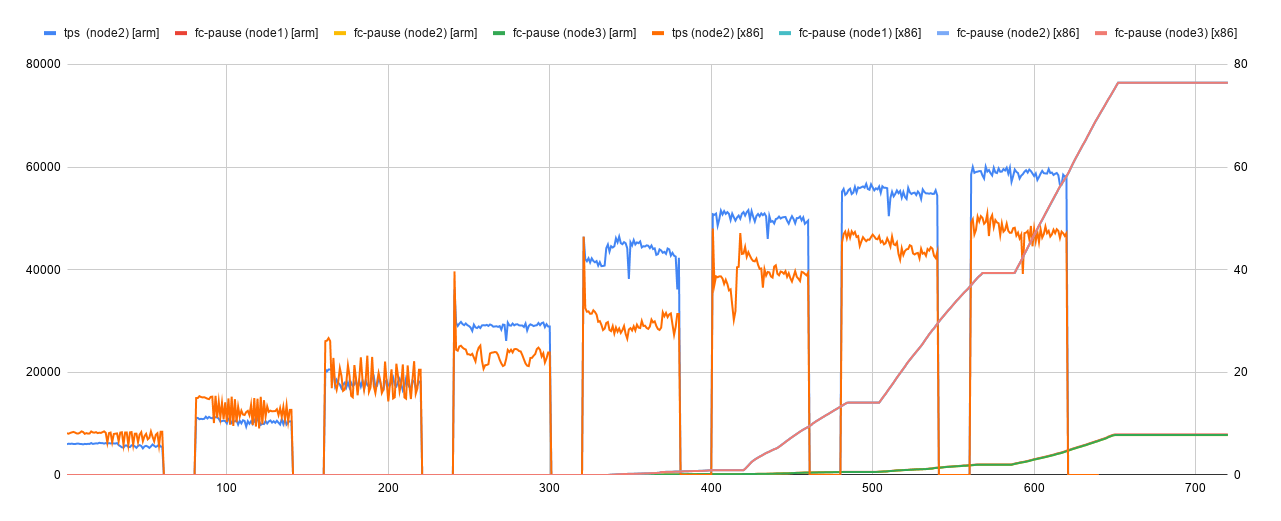 left-y axis tracks qps/tps, right-y axis flow-control-pause (in seconds) and x axis timeline
left-y axis tracks qps/tps, right-y axis flow-control-pause (in seconds) and x axis timeline
observations
- mariadb on arm continues to scale better and importantly maintain a low flow control pause as expected since other nodes are not processing any other workload.
write-to-all-nodes
benchmarking pattern
- write workload is made active on all the nodes. This means each node will process write and also replicated write-sets from other 2 nodes. There could be conflict and each node also has to perform conflict resolution. Real test of compute power.
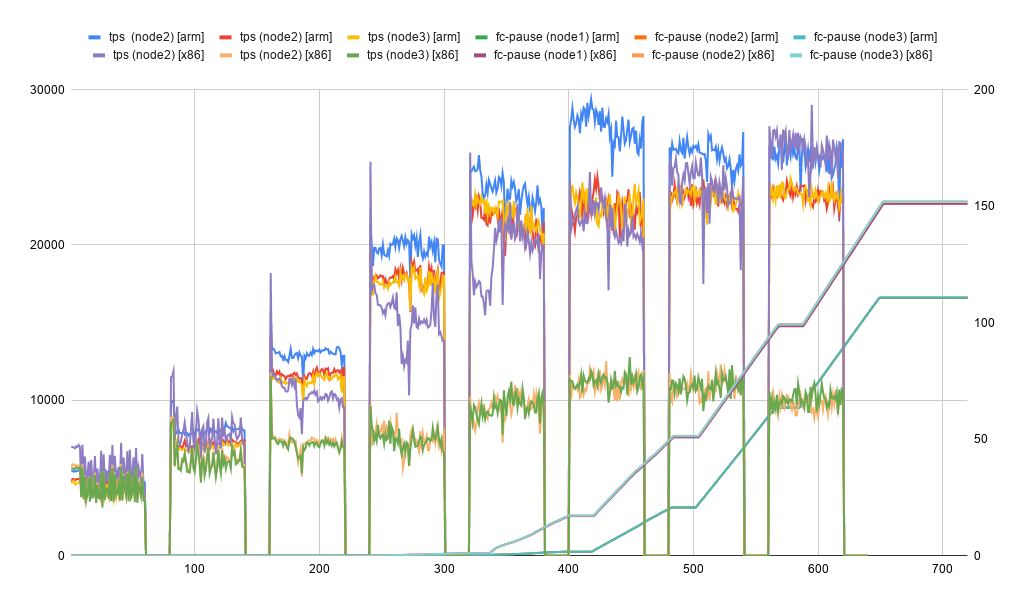 left-y axis tracks qps/tps, right-y axis flow-control-pause (in seconds) and x axis timeline
left-y axis tracks qps/tps, right-y axis flow-control-pause (in seconds) and x axis timeline
observations
- arm is able to scale better than its counterpart. What is also worth noting is that all 3 arm nodes are able to maintain around the same throughput vs the counterpart where-in one of the nodes has better throughput and other nodes showed some serious performance lag.
Conclusion
This once again helps re-establish the needed confidence that whatever is your setup topology (master-slave or multi-master) migrating MariaDB to ARM is beneficial from both cost and performance perspective. So when are you considering moving to ARM?
If you have more questions/queries do let me know. Will try to answer them.
